Unlocking the potential of small RNAs (sRNAs) in drug development
Fastest growing area of research
growth in sRNA focused publications over the last decade1
of clinical trials in 2020 used sRNA2
RNA drugs in active clinical trials3
FDA Approved RNA therapeutics4
Successful drug development requires a comprehensive view of sRNA biology
Powerful...
sRNA regulates all gene expression, driving disease and maintaining health
…but Complex
Current approaches miss important aspects of sRNA biology
- Annotation of transcript variants and non-templated nucleotides
- Predicting regulatory targets and mechanism of action
- Differential regulatory targets based on sRNA variants
- Extracellular and cellular sRNA localization signals
Starting at the source: how sRNA isoforms drive disease3
SRNAS ARE MASTER REGULATORS OF GENE EXPRESSION FOUND IN BLOOD AN D TISSUE
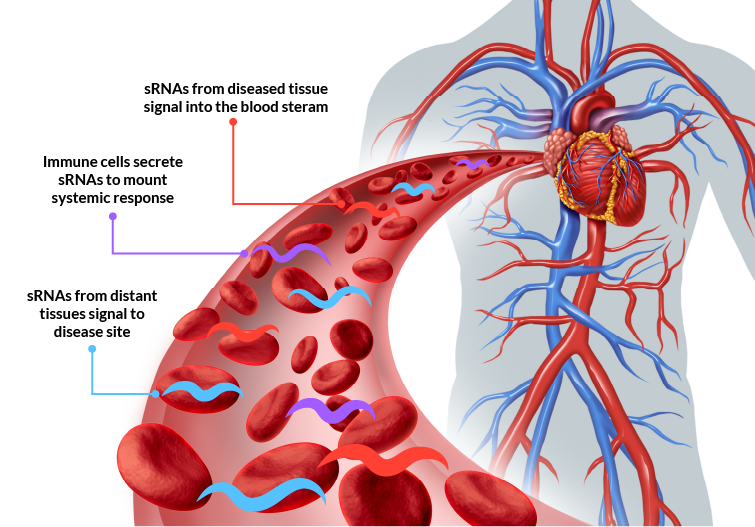
Small RNAs control every biological pathway and process
Deregulation of small RNAs causes and drives diseases
Unique expression patterns in tissues and cell types enable classification
Present in every matrix
Easily extracted and very stable in samples
GUIDED BY THE RISC COMPLEX, NON-CODING sRNAs IN THE GENOME MODIFY PROTEIN EXPRESSION
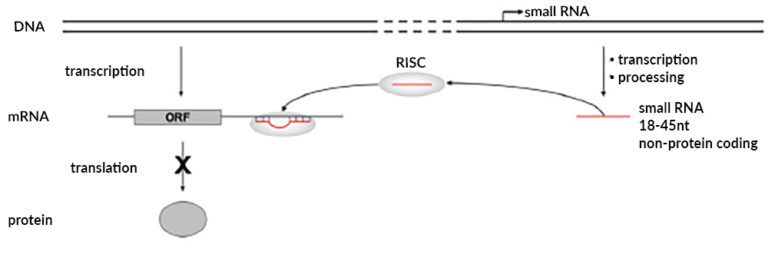
ANALYSIS OF RISC SHOWS THERE ARE MANY CLASSES OF FUNCTIONAL SRNAS
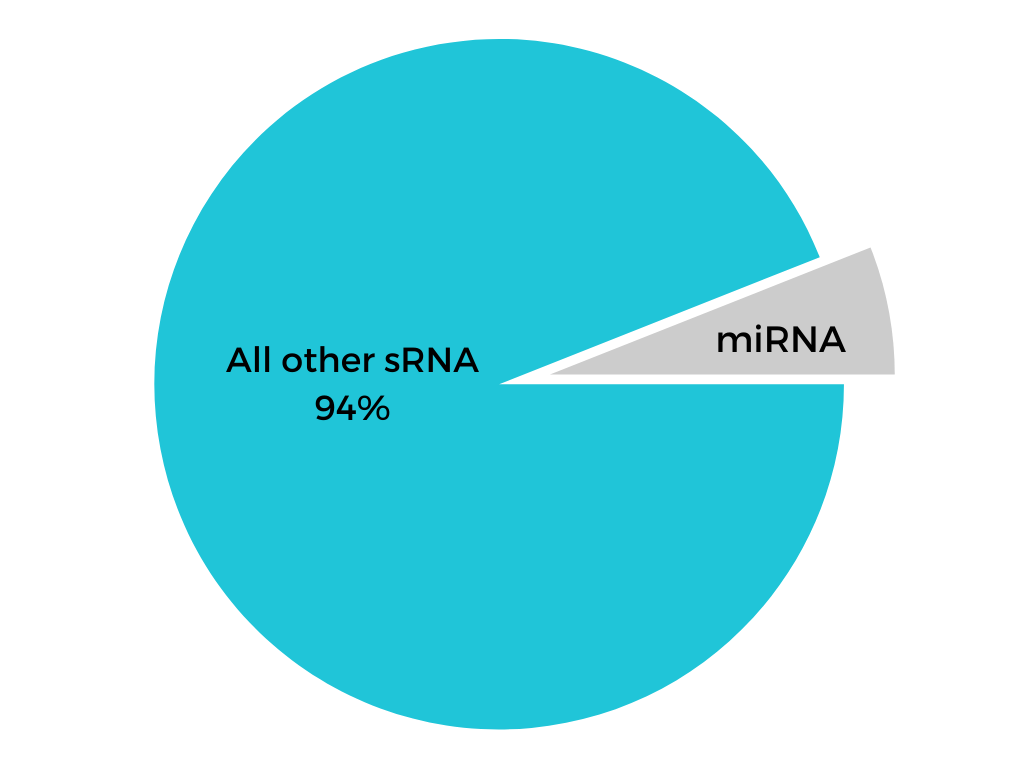
Only 6% of non-coding sRNAs contained in the RISC complex are miRNA
VARIATIONS IN POST TRANSCRIPTIONAL PROCESSING OF SRNAS DRIVE DISEASE BY DISRUPTING PROTEIN EXPRESSION

sRNA analysis requires single nucleotide fidelity
'Seed' sequence – directs RISC to target site RNA
Isoforms that shift the 'Seed' sequence causing regulation of the wrong proteins
NEXT: Check out our pipeline
REFERENCES:
1. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Accessed June 16, 2021. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
2. National Library of Medicine. Accessed June 16, 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/
3. Data on file, Gatehouse Bio; 2021.
4. The ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. 2012;489:57-74.
